History of Balinese Painting and Some of Its Characteristics:
Balinese painting has strong and distinctive characteristics that are deeply rooted in the island’s culture. Like many other art of Bali, such as music, dance, sculpture, and painting, Balinese painting has a rich history. In addition to its history, Balinese painting exhibits several distinctive characteristics.
Long History of Balinese Painting style:
The journey of Balinese painting has evolved over time to become the art we recognize today. It spans from prehistoric times through the colonial period and into the modern era.
The following is a summary of the history of Balinese painting based on the Journal of Urban Society’s Art Volume 3 No. 1, April 2016, and research conducted by FPRD Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia.
Prehistoric Era in Indonesia:
Bali’s ancestors have been inhabiting the island for thousands of years before the Common Era. During that time, the community engaged in various artistic expressions primarily for their ritual ceremonies.
They created artworks like stepped pyramids (punden berundak), dolmens, and sarcophagi. Over time, the traditional art of painting began to develop.
Pre-Colonial Period:
Before the arrival of Javanese kingdoms that dominated Bali, the pre-colonial period involved the use of Balinese painting for Hindu religious activities.
Paintings were utilized to adorn temples (pura) or the houses of the upper-caste members of Balinese society. Artworks featured deities, epics, legendary figures, and heroes.
Balinese paintings during this era were dominated by colors such as red, golden yellow, white, and black, symbolizing their beliefs. For example, red symbolized the creator deity Brahma, white represented the preserver deity Vishnu, and black represented the deity Shiva.
Colonial Period to Classical Period:
Bali was once a colony of Javanese kingdoms, particularly under the rule of the Hindu Mataram Kingdom led by King Sanjaya (732 CE). This period coincided with the classical art period in Java (7-9 CE), influencing Balinese art significantly.
After the decline of the Syailendra Dynasty, Bali was ruled by native Balinese kingdoms. However, it later came under the control of the East Javanese kingdom, led by Airlangga (1014-1047). This period saw the development of architectural artworks like Gunung Kawi Temple, Bukit Darma and Goa Gajah.
Bali regained independence after Airlangga’s death but later fell under the rule of the Majapahit Kingdom from 1222 to 1292. The influx of Majapahit refugees to Bali contributed to the strong influence of Javanese Hindu culture. Despite this influence, the Balinese people made efforts to preserve their distinctive identity, enriching Balinese art.
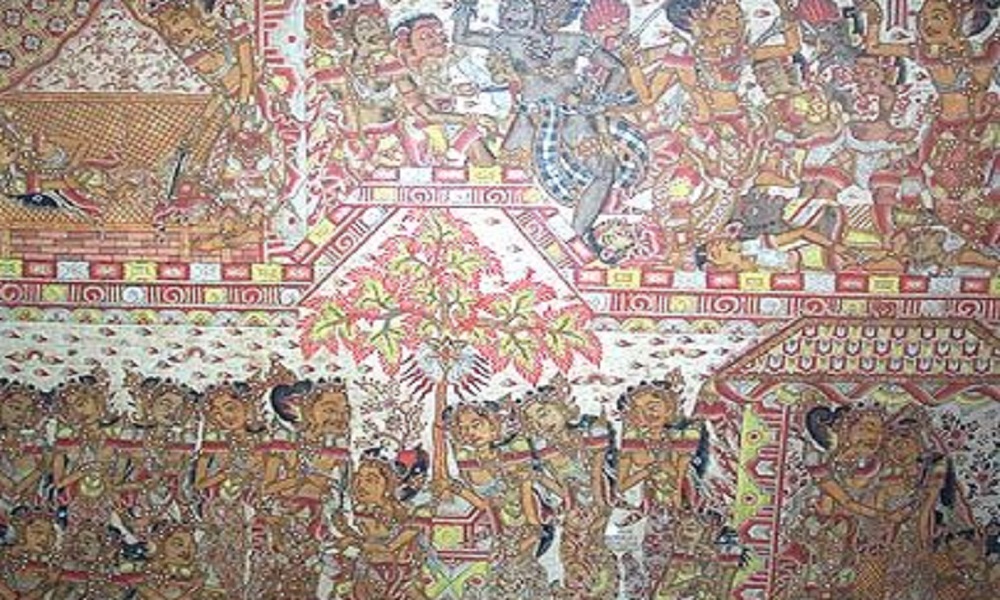
The peak of classical Balinese painting occurred during the reign of Dalem Watu Renggong in the 17th to 18th centuries, especially with the emergence of pioneering artists like I Gede Mersadi, also known as Sangging Modara, who contributed the styles of Balinese Painting that is wayang paintings from Kamasan.
Modern Period:
Bali’s art entered the modern era with the arrival of the Dutch in Indonesia. Western culture brought by the Europeans was embraced by the Balinese, adding new dimensions to Balinese art.
Dutch artists, including Rudolf Bonnet, Le Mayeur, W.G. Hofker, Romualdo Locatelli and Walter Spies visited Bali. In 1932, the European-Balinese art group called Pita Maha was formed by Rudolf Bonnet, Cokorda Gede Agung Sukawati, Walter Spies, Cokorda Gede Rai Sukawati Cokorda Gede Raka Sukawati and I Gusti Nyoman Lempad. Pita Maha aimed to stimulate art and generate interest among its members. Their artworks were selected by art experts and sold, with only a small portion of the profits used for operational expenses.
What is Balinese Painting style?:
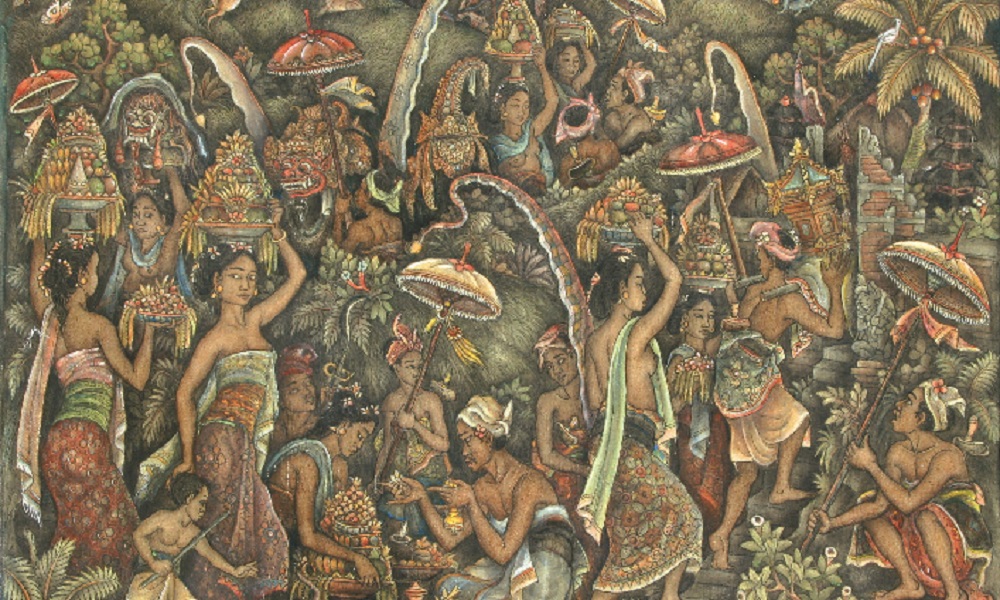
What Is the Style of Balinese Art? Since the emergence of Pita Maha, which brought Balinese painting into the modern era, their artworks have inspired subsequent generations. The styles of Ubud, Sanur and Batuan emerged as significant influences.
Ubud Balinese Painting:
Balinese Paintings Ubud is influenced by Spies and Bonnet, the Ubud style features dynamic composition, perspective, and color choices. It introduced the use of Western painting materials and tools, such as watercolors, oil paints, and tempera. The influence is also seen in the play of light and shadow.
Batuan Painting Style:
The Batuan style is known for its eerie nighttime atmosphere, featuring strange-looking ghosts, mythical creatures, witch-like figures, and blood-sucking corpses. This style incorporates elements of traditional wayang puppetry, with frontal depictions of human figures and additional elements like mountains and trees for perspective.
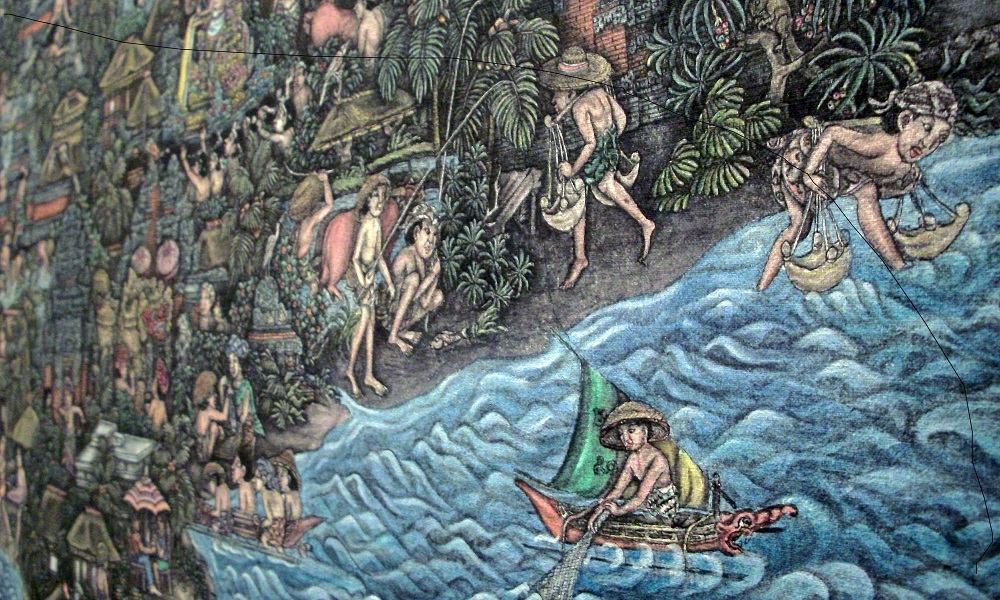
Sanur Painting Style:
The Sanur painting style draws inspiration from the sea and daily life. Many artists depict marine life, sea creatures, turtles, crabs, and bathing scenes. Notable artists practicing the Sanur style include Ida Bagus Nyoman Rai and I Ketut Regig.
In conclusion, this explanation covers the history of Balinese painting from the prehistoric era through the Hindu Javanese colonial period, the classical period, and into the modern era. The art developed and gave rise to the Batuan, Sanur and Ubud styles.
Balinese Painting for sale:
If you are interested in purchasing Balinese Painting in Indonesia, there are various avenues and platforms where you can explore and find artworks for sale. When purchasing Balinese paintings, it’s essential to verify the authenticity of the artwork and ensure that you are dealing with reputable Bali handicrafts Suppliers. If you are buying from galleries, online platforms, or art dealers, inquire about the artist’s background, the provenance of the artwork, and any accompanying certificates of authenticity. Additionally, clarify details such as shipping, payment methods, and return policies before making a purchase.